ITSM: The Definitive Guide
Discover the meaning of ITSM, its benefits, capabilities, best practices, and how to find the best ITSM tool.

ITSM: The Definitive Guide
There is much to say about IT Service Management (ITSM). We have learned a lot during our time working in the field, and there is surely still more to incorporate in the years ahead.
This domain constantly grows, changes, and evolves, sometimes making it hard to keep up with all the new information and latest ITSM trends. That’s why we designed this definitive guide to the world of IT Service Management and why we are constantly putting efforts into keeping it updated.
If you are new to the ITSM world, welcome aboard! It’s going to be an exciting journey. If you have spent time in ITSM, or if you are already a professional or even an expert, we believe you will find valuable insights here too.
This guide serves as a gateway and a resource for the ITSM community. No matter your level of experience or expertise, we will cover ITSM from start to finish, addressing everything from basic concepts to more complex ones.
Welcome to the ITSM Definitive Guide!
What is ITSM?
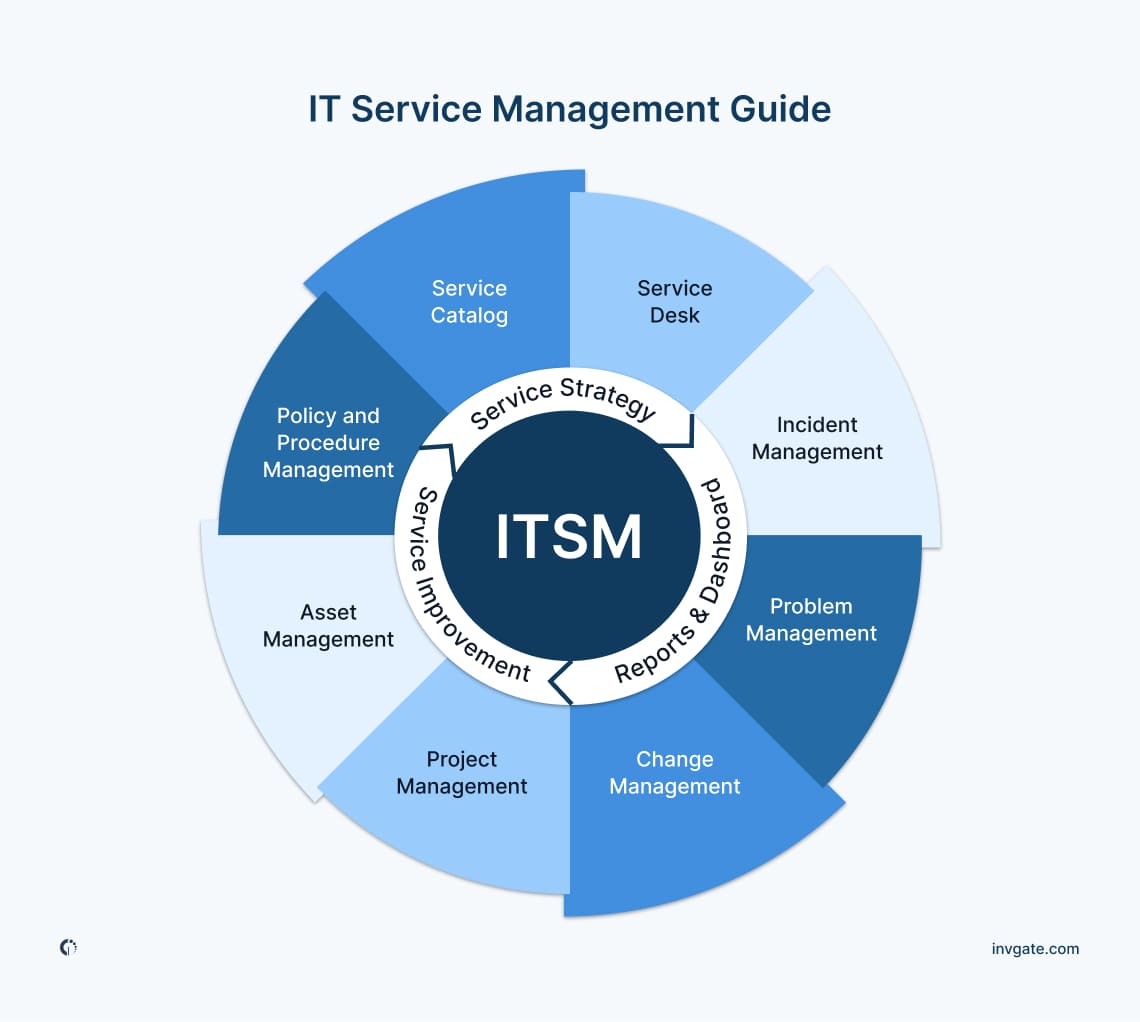
Information Technology Service Management or simply IT Service Management is how IT teams design, deliver, manage, and improve end-to-end IT services for employees, clients, or customers. This definition emphasizes an important core concept of ITSM: the belief that IT should operate as a service through processes, practices, and tools.
If you prefer a more formal explanation, ITIL 4 – the most popular ITSM framework – defines it as a “set of specialized organizational capabilities for providing value to customers in the form of services.” This definition is similar to the first one but emphasizes the focus on value.
If you are just learning about this concept, this definition might seem confusing at first. So, let’s break it down with a simple example. Imagine you work at a company, and your computer suddenly stops working (a completely plausible IT scenario). You contact the IT department, and they quickly help you fix the problem so you can get back to work. This process of managing and resolving your issue is at the core of ITSM. In this example, fixing the laptop is one of the many IT services the IT team provides.
However, it’s not just about managing technology through a set of best practice processes. ITSM encompasses capabilities that also improve business operations and outcomes while providing real value.
For this, ITIL 4 (as other frameworks) offers a comprehensive list of capabilities to help guide organizations through the process. We will summarize them in the following paragraphs.
But first, and to complete our definition, it’s important to differentiate ITSM from a range of other well-known acronyms in the industry: ITIL, ITAM, ITOM, ESM, and CRM.
ITIL vs. ITSM
ITIL (formerly known as Information Technology Infrastructure Library) is a framework – one of many – that offers best practices for IT Service Management. While ITSM encompasses the entire discipline of managing and delivering IT services to meet business needs, ITIL provides a structured approach to implementing ITSM.
ITAM vs. ITSM
ITAM (or IT Asset Management) and ITSM intersect (and work best together) but have distinct focuses. ITAM deals with the Lifecycle Management of IT assets — everything from procurement to disposal — ensuring that all IT assets are used efficiently and aligned with business needs.
ITSM, on the other hand, is broader, focusing on the delivery and management of IT services, which can include the use of these assets but also covers processes, people, and technologies involved in service delivery.
ITOM vs. ITSM
ITOM (IT Operations Management) is focused on the administration and management of IT infrastructure and operational tasks, which are essential for the smooth running of IT services.
ITSM, however, is concerned with the overall management and delivery of IT services, including planning, designing, and improving those services. ITOM supports ITSM by ensuring that the underlying IT infrastructure is functioning optimally.
ESM vs. ITSM
Enterprise Service Management (ESM) extends the principles and practices of ITSM beyond IT, applying them to other business areas like Human Resources, Finance, and Facilities Management.
While ITSM is specifically focused on managing and delivering IT services, ESM uses the same frameworks and processes to improve Service Management across the entire enterprise. The key difference is in scope: ITSM is confined to IT, while ESM brings a unified approach to Service Management across various departments.
Just a note: You might have heard of ESM as shared services, which refers to a similar approach.
CRM vs. ITSM
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and ITSM serve different purposes but can intersect when IT services are customer-facing. The former focuses on managing a company’s interactions with current and potential customers, aiming to improve customer satisfaction and retention. The latter is about managing and delivering IT services within an organization.
The two can overlap in scenarios where IT services are directly involved in supporting customers, such as in help desks or customer support systems, but CRM is centered on customer interactions, while ITSM is centered on Service Management within IT.
Why is IT Service Management important?

IT Service Management can benefit your entire company. It leads to efficiency and productivity gains. It also ensures that IT services align with business goals, reduce costs, and improve service quality.
By adopting ITSM practices, companies can better manage their IT infrastructure, streamline processes, and deliver consistent, reliable services to both internal and external users.
The benefits of ITSM
ITSM offers benefits on multiple levels. It can help individuals to discharge their responsibilities more efficiently and effectively. It can help IT service providers to deliver better IT support to employees and external customers. And it can help businesses to better use technology as both an enabler and competitive differentiator and provide better products and services to customers.
There are many ITSM benefits. We made a short list to convey what we think are the most significant:
Reduced costs and more efficient IT budgeting.
Improved quality of IT services and support that positively affects employees and customers and business outcomes.
Increased competitive advantage through better IT enablement.
Increased agility/speed of change to meet new business needs.
- Improved governance, risk, and compliance.
- A focus on continual improvement.
Contribute in Digital Transformation processes.
Most common ITSM frameworks
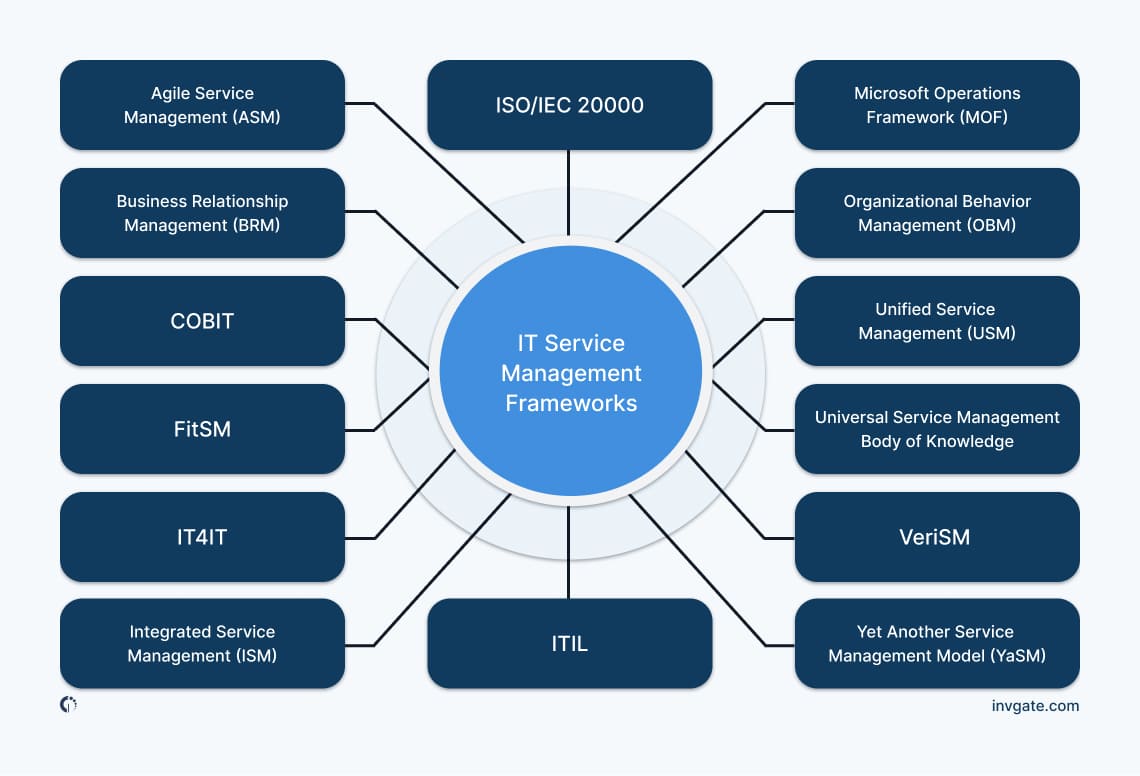
ITSM can use frameworks to provide structured approaches and best practices for delivering IT services that align with business needs. Understanding the various ITSM frameworks available is essential for organizations because each one offers unique methodologies.
The three most common ITSM frameworks are ITIL, COBIT, and ISO/IEC 20000. Let’s see them in more detail.
ITIL
ITIL is the most widely adopted framework. It provides a comprehensive set of best practices for managing IT services throughout their lifecycle, from strategy and design to operation and continuous improvement. ITIL focuses on aligning IT services with the needs of the business.
COBIT
COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies) is a framework developed by ISACA for IT Governance and Management. It provides a set of practices for managing and controlling IT operations, ensuring that IT aligns with business goals, manages risks, and complies with regulations.
ISO/IEC 20000
ISO/IEC 20000 is an international standard for IT Service Management. It specifies the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an ITSM system. Organizations that comply with ISO/IEC 20000 can be certified, demonstrating their commitment to high-quality IT service delivery.
These frameworks are designed to enhance efficiency, service quality, and customer satisfaction in different ways. By adopting one or more of these, companies can standardize their processes, improve service delivery, and ensure compliance with industry standards.
For those looking to dive deeper into these frameworks, we designed a free downloadable ITSM frameworks cheat sheet that provides a quick reference to the key features and benefits of each ITSM framework.
ITIL principles for ITSM and ITSM practices
In the world of ITSM, the diversity of frameworks, methodologies, and company cultures means that best practices and principles can vary widely. Each framework, such as ITIL, COBIT, or ISO/IEC 20000, offers its own set of guidelines and recommendations tailored to specific objectives.
Additionally, companies and individual teams often develop their own best practices and principles based on their unique challenges, goals, and operational environments.
Despite these differences, there are certain best practices and principles that are universally recognized across all frameworks and organizations. These commonalities stem from the shared goals of improving service quality, efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
By focusing on these core elements, organizations can ensure that their ITSM practices align with industry standards while still allowing for the necessary adaptations to fit their specific needs.
Below are ten of the most common ITSM best practices and five of the most common principles that are widely accepted across various frameworks.
Most common ITSM best practices:
- Continual service improvement: Regularly evaluate and refine IT services to adapt to evolving business needs.
- Customer-centric approach: Always prioritize the needs and experiences of the end-users.
Change Management: Implement structured processes to manage changes effectively, minimizing disruptions.
Incident Management: Develop efficient processes to identify, analyze, and resolve incidents promptly.
Knowledge Management: Capture and disseminate knowledge to improve decision-making and service delivery.
Service Level Management: Define, monitor, and review service levels to ensure they meet business expectations.
Problem Management: Identify and manage root causes of incidents to prevent recurrence.
Configuration Management: Maintain accurate records of IT assets and configurations to support efficient operations.
IT Asset Management: Track and manage IT assets throughout their lifecycle to optimize their value, ensure compliance, and support decision-making.
Service Catalog Management: The purpose of the Service Catalog Management practice is to provide a single source of consistent information on all services and service offerings.
Most common ITSM principles:
- Value to customers: Focus on delivering value and meeting or exceeding customer expectations.
- Alignment with business goals: Ensure IT services are aligned with and support the organization’s overall objectives.
- Collaboration and communication: Promote open communication and teamwork across all departments and teams.
- Governance and accountability: Establish clear roles, responsibilities, and policies for IT management and operations.
- Sustainability: Focus on long-term strategies that ensure IT services are resilient, efficient, and capable of supporting future growth.
How to implement the IT Service Management framework
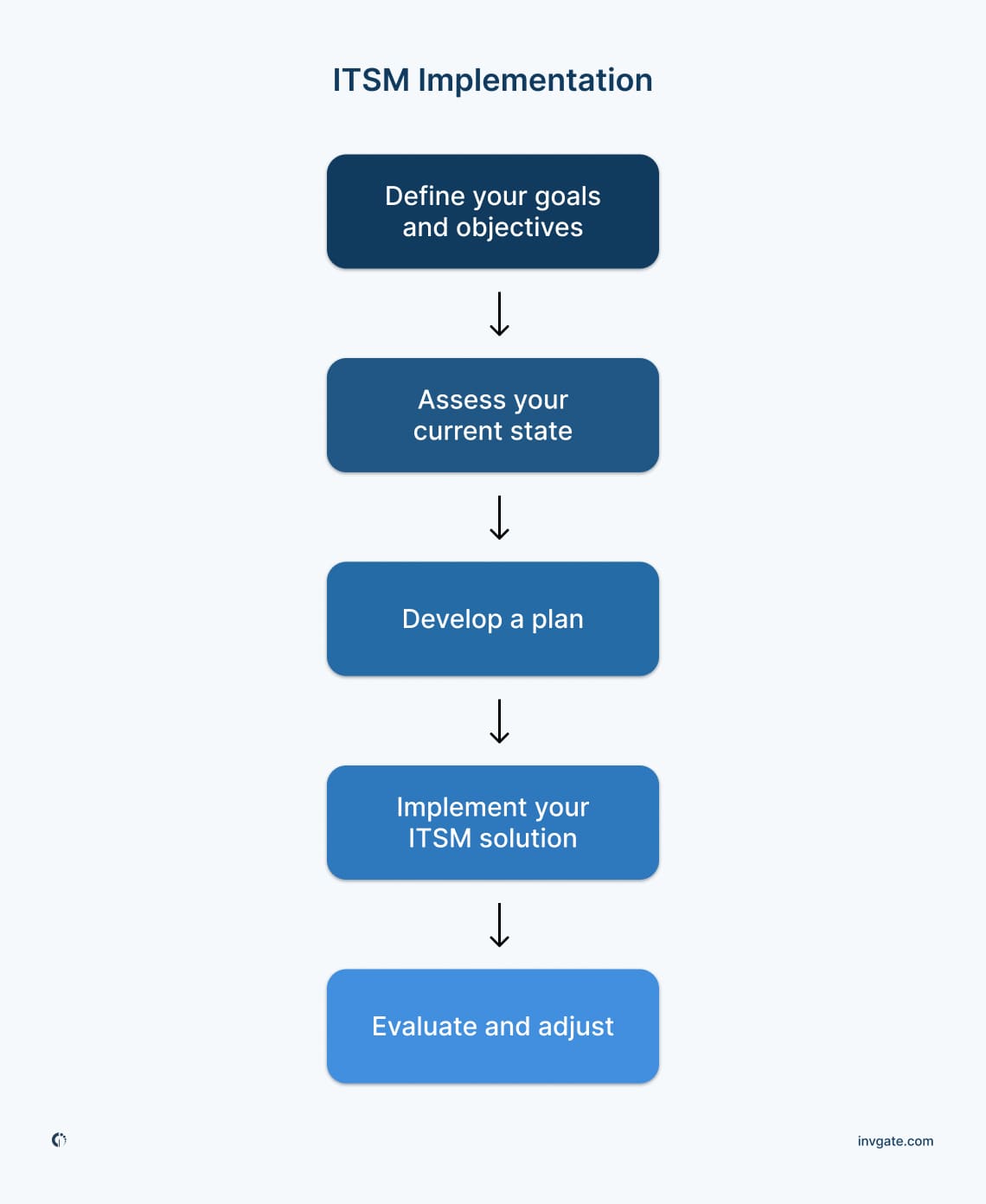
Implementing an ITSM framework requires a structured approach to ensure that processes align with organizational goals and meet customer needs effectively.
To help you out, we have created a thorough ITSM implementation checklist, which serves as a comprehensive guide to help organizations identify critical steps in the process.
This checklist typically includes defining objectives, assessing current processes, selecting the right ITSM tools, training staff, and establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure success. By following it, organizations can streamline their implementation efforts and minimize potential pitfalls.
Step-by-step implementation process
- Define your goals and objectives: Including specific business outcomes, improvements in service delivery, and alignment with organizational goals, ensuring that they are measurable and time-bound.
- Assess your current state: Conduct a thorough assessment of your existing IT infrastructure, processes, and capabilities to identify strengths, weakness, es, and gaps that the ITSM implementation needs to address.
- Develop a plan: Outline the steps, resources, timelines, and roles needed to achieve your goals (our checklist can help!), ensuring alignment with industry best practices and compliance with any regulatory requirements.
- Implement your ITSM solution: Choose a tool that meets your needs, goals, and budget. A good way to compare different options is sending out an ITSM RFP. For implementation, make sure you are providing necessary training to staff, while maintaining clear communication to ensure smooth adoption and minimize disruption.
- Evaluate and adjust: Continuously monitor the performance of your ITSM solution against the defined objectives, gathering feedback, and making necessary adjustments to optimize effectiveness and address any emerging challenges or opportunities for improvement.
Keep in mind this is just a quick recap. Since the process can be a little bit challenging, you’ll find each step broken into 18 tasks on the checklist above, along with the corresponding subtasks and deliverables. We also added a space for you to assign a person responsible and a deadline for each one of them.
Using InvGate Service Management as your ITSM tool
InvGate Service Management is not just a powerful ITSM tool; it’s a game-changer that can elevate Service Management across your entire company.
Its features and no-code capabilities allow you to extend all these benefits to every department, also transforming it into an all-encompassing Enterprise Service Management solution.
You don’t have to just trust us on this one! InvGate Service Management was featured in the first edition of their 2024 Market Guide for IT Service Management (ITSM) platforms created by the IT Consulting and Research firm Gartner.
Here’s a closer look at the features that make this tool the ultimate choice for ITSM — and beyond:
- Ticket Management: Efficiently handle and resolve user requests with a robust Ticket Management system. It centralizes all requests in one place, ensuring nothing falls through the cracks. Prioritize, categorize, and track progress seamlessly to enhance service delivery.
- Analytics: Gain deep insights into your service desk performance with powerful analytics, dashboards and reports. Track key metrics, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions to continuously improve your ITSM processes. With clear visualizations, you can easily spot areas for improvement and optimize your operations.
- Self-service: Empower users to find solutions on their own with an intuitive self-service portal. By accessing a rich knowledge base and submitting requests directly, users can resolve issues faster, reducing the load on your IT team. This feature enhances user satisfaction while streamlining service operations.
- Artificial intelligence (AI Hub): Leverage the power of AI with InvGate AI Hub to enhance your agents' support abilities. These functions enable them to summarize requests, improve ticket responses, and even automatically draft knowledge base articles, to name a few.
- Workflows: Customize and optimize help desk workflows to match your organization’s unique processes. Whether for ITSM or other departments, InvGate Service Management no-code workflow builder allows you to design workflows that enhance collaboration and ensure smooth operations. This flexibility and customization capabilities makes it a powerful tool across the enterprise.
- ITIL-aligned: Adhere to industry best practices with ITIL-aligned processes that ensure efficient and effective IT Service Management. InvGate Service Management’s ITIL alignment supports continuous improvement in your ITSM activities.
- Multiple department support: Extend the benefits of InvGate Service Management beyond IT to other departments in your organization. By building and integrating multiple help desks within the tool, you can manage HR, Facilities, Finance, and more, all from a single platform. This transforms InvGate Service Management into a powerful ESM tool, unifying Service Management across the entire company.
How to measure ITSM? Top ITSM metrics to track
There are numerous metrics in ITSM (also known as help desk metrics). Each one plays a critical role in assessing different aspects of service delivery and performance. These metrics help organizations gauge efficiency, effectiveness, and overall service quality, providing insights that drive continuous improvement.
While there are many to consider, here are five essential ITSM metrics you should be tracking:
- First Call Resolution (FCR): This metric measures the percentage of incidents resolved on the first contact with the service desk.
- Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR): MTTR tracks the average time it takes to resolve an incident from the moment it is reported.
- Change Success Rate: This metric measures the percentage of changes implemented without causing incidents or requiring rollback.
- Ticket Volume: Incident volume tracks the total number of incidents logged over a specific period.
- Service Level Agreement (SLA) Compliance: SLA compliance measures the percentage of incidents resolved within the agreed time frames.
How to use AI in ITSM
AI is rapidly transforming the landscape of IT Service Management, offering new ways to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and user satisfaction. As organizations seek to streamline operations and improve service delivery, AI emerges as a powerful tool that can automate routine tasks, provide predictive insights, and enhance decision-making.
However, from our perspective, AI should be at the service of IT teams, and be used to enhance their capabilities. With that in mind, InvGate Service Management AI Hub offers the following key features:
- AI Ticket Summarization: This feature can create a brief ticket summary with the incident’s main activity. This can shorten the time it takes to onboard someone new to a complex ongoing incident by up to 90% (from 10 minutes to less than 1 minute).
- The Knowledge Article Generation: This capability transforms incident resolutions into knowledge articles. After resolving an incident, agents will get the chance to use the details from the initial request and the most relevant activity to solve it and generate a first knowledge article draft with AI.
- AI-Improved Responses: This feature leverage generative AI to improve, shorten, or expand help desk agents’ ticket replies.
- Contextual Knowledge Article Summaries (by Virtual Agent): InvGate Service Management Virtual Agent can provide end-users with contextual knowledge article summaries so that they quickly get the information they need to solve an issue without contacting IT support.
By incorporating these capabilities, InvGate Service Management is not only enhancing ITSM but also paving the way for a more intelligent and proactive approach to Service Management.
In conclusion
As we wrap up our journey through IT Service Management, it's clear that ITSM is more than just a framework, more than just a set of best practices and principles. It’s also more than just a tool.
ITSM is a comprehensive approach to aligning IT services with business goals, improving efficiency, and driving value across the organization. Here are the some key takeaways to remember:
- ITSM is foundational to modern IT operations, providing structured processes to deliver and manage IT services that meet business needs.
- Understanding ITSM frameworks like ITIL, COBIT, and ISO/IEC 20000 is a good starting point, as they offer best practices and guidelines for effective ITSM implementation.
- Investing in ITSM yields significant benefits — from reducing costs and improving service quality to increasing agility and customer satisfaction.
By mastering these core concepts, you're well on your way to leveraging ITSM for greater business success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Check out InvGate as your ITSM and ITAM solution
30-day free trial - No credit card needed





